Introduction :CNC milling is a cutting process performed on CNC milling machines or machining centers. By rotating the milling cutter at high speed along a preset path, it processes materials to form parts that meet design specifications. This article provides a systematic overview of CNC milling, covering its definition, processing advantages and limitations, as well as its application scope, to help you quickly grasp this technology.
I. What is CNC Milling
CNC milling is a precision machining process that uses a CNC system to drive a milling machine, cutting materials with programmed precision. It can process various materials including plastics, hard metals, and soft metals, and is commonly used to create flat surfaces, contours, grooves, holes, and complex 3D structures. Many products we see in our daily lives are made using this process, such as the interfaces and grooves of electronic products, or the sliding grooves of doors and windows.
To explain further, CNC milling can be understood in two parts.
First comes milling, which involves cutting material using a high-speed milling cutter. This process can excavate grooves within the material, smooth out rough surfaces, or perform more intricate machining to transform the material into a three-dimensional shape.
Next is CNC machining, which essentially involves inputting instructions into the machine rather than manually cutting objects with tools. This ensures that upon receiving commands, the machine controls the milling cutter’s operational path and regulates the width and depth of the cut.

II. CNC Milling Process
The CNC milling process typically involves multiple steps, as detailed below:
Step 1
First, using CAD (computer-aided design) software, create an ideal model of the component.
Step 2
CAD models are input into CAM (computer-aided manufacturing software), which generates machining code based on the product model. This code serves as a digital instruction set, precisely defining the milling cutter’s working path, material cutting depth, coordinate positions, and feed rates to ensure the production of parts conforming to the intended structural specifications.
Step 3
Debugging the CNC milling machine (a machine that cuts materials and modifies their shape using milling cutters). This process involves placing the workpiece and raw material on the machine, measuring and achieving precise positioning to complete the debugging of the CNC milling machine.
Step 4
Initiate the programme to run the machining sequence in a continuous loop. The milling cutter operates at high speed according to the pre-set programme, cutting away excess material from the workpiece until it precisely matches the dimensions specified in the design drawings.
III. Common Equipment for CNC Milling
The core equipment for CNC milling includes milling machines and machining centers. According to the number of axes, commonly used CNC milling machines are categorised into three-axis, four-axis, and five-axis types, catering to machining requirements ranging from planar features to complex curved surface components.
- Three-axis milling machines drive the cutter along the X, Y, and Z linear axes for cutting operations, suitable for machining relatively simple-shaped components.
- Four-axis milling machines incorporate an additional rotary axis to rotate the workpiece, expanding the machining capabilities of three-axis machines by adding rotational processing functionality.
- Five-axis milling machines feature a total of five axes of motion, incorporating two additional rotary axes beyond standard three-axis machines. This configuration enables the machining of complex curved surfaces and irregularly shaped components.
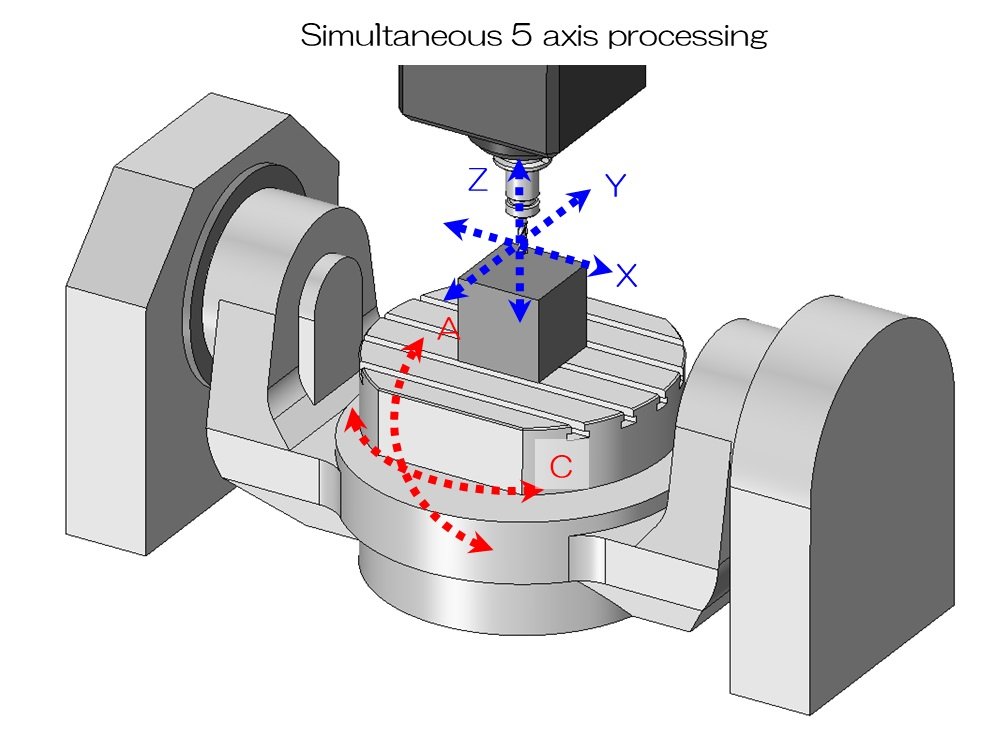
IV. What Materials can be Machined by CNC Milling?
CNC milling can process three types of materials: plastics, soft metals, and hard metals. Among these, aluminum alloys and low-carbon steel are particularly favored due to their ease of machining. Other common materials include aluminum alloys 6061 and 7075, stainless steels 304 and 316, as well as plastics such as ABS, PC, POM, and nylon.
However, materials that are either too hard or too soft are not suitable for milling, as they may lead to uncontrollable adverse reactions and reduced cutting accuracy of the milling cutter.
V. Application of CNC Milling
CNC milling has extensive practical applications, primarily covering automotive, electronics, industrial machinery, aerospace, and even household items. The components required in these industries are characterized by high precision or small dimensions. Common examples include:
Automotive industry:
engine block, gearbox valve block, steering knuckle, sub-frame, window guide rail
Electronics:
metal frame, camera mount, port slot, hard drive bracket, sensor housing
Industrial equipment:
machine tool bed guide rails, fixtures and jigs, valve body flow channels, valve cores
Aerospace:
Engine components, fuselage structural parts, spacecraft structural components
VI. Advantages of CNC Milling
CNC milling is a new main force in manufacturing industry, which has its own unique advantages, mainly reflected in high precision, can process complex parts, high efficiency, etc.The specific content are as follows:
High machining accuracy
First, CNC milling offers high machining accuracy. When this process is applied, it significantly improves part precision, making products better suited for industries with stringent accuracy requirements.
Machining complex parts
CNC milling can process parts with high complexity. High difficulty processes such as curved surfaces, grooves, and pattern engraving can all be achieved through CNC milling.
High processing efficiency
CNC milling offers the advantages of high efficiency and minimal material loss. Compared to manual processing, it only requires inputting the design drawings to generate machining codes, significantly reducing the labor input. Moreover, the production of defective parts due to technical issues or subjective factors is greatly minimized.
Wide range of material selection
A wide range of materials can be used, including not only hard metals but also plastics and wood. As long as the material properties match the cutting parameters, stable machining can be achieved to meet the part manufacturing needs of various industries.
Moldless machining
CNC milling eliminates the need for pre-made molds, dramatically cutting processing costs. This makes it ideal for rapid prototyping and iterative development.

VII. The Disadvantages of CNC Milling
The CNC milling technology is not perfect, and there are some defects, including economic and technical, mainly reflected in the following points:
High upfront investment costs
The expenses for equipment procurement, programming software acquisition, and site debugging are substantial, resulting in significant initial financial outlay.
Small-batch simple parts have poor cost-effectiveness.
The preparation time for programming, clamping, and tool setting far exceeds the actual machining time of the parts. If the number of parts to be processed is very small, the cost-effectiveness becomes relatively low.
The machining efficiency of hard materials is low
When machining cemented carbide, high carbon steel and other materials, the tool wears out quickly, and the speed of the machine tool is reduced, which leads to the prolongation of machining cycle.
VIII. Why CNC Machining?
In the manufacturing industry, why has CNC milling become the preferred choice for more factory operators over other traditional processes? The reason lies in its superior advantages in precision, strength, surface quality, and batch consistency compared to other techniques, as detailed below:
- Compared with 3D printers, CNC milling delivers superior machining intensity, resulting in parts with enhanced texture and higher quality.
- Compared with injection molding, CNC milling eliminates the cost of molds, making it a more cost-effective option for small-batch production.
- Compared with die casting, CNC milling has higher speed and can achieve better results when facing complex parts.
- Compared with turning, NC milling is more suitable for non-rotating and symmetrical parts.
Conclusion
CNC milling is a precision machining process that uses a CNC system to drive a milling machine, cutting materials with preset programs. It can process various materials including plastics, hard metals, and soft metals, covering multiple industries and handling both complex and simple parts. This technology combines high precision, efficiency, broad material applicability, and the ability to handle intricate designs. However, it also has limitations such as high initial investment and time-consuming operator training. Compared to 3D printing and injection molding, CNC milling offers unique advantages in part strength, cost-effectiveness, and complex component processing, making it a representative of the rapid advancement in modern manufacturing technology.
As a global precision manufacturing provider, Keywin offers professional CNC Milling services with full support for small-batch production starting from just one piece. We provide rapid drawing evaluations, flexible material options, and one-on-one technical support from our experienced engineers.
When you’re ready, send your drawings—we’ll get you a quote today.


